|
||
|
Link to share: https://hanglberger-manfred.de/en-erde-entstehung.htm
Where does the earth come from? - The origin of a life-friendly planet A compilation by Manfred Hanglberger
(www.hanglberger-manfred.de) |
||
|
|
1. Big Bang The universe was created from a tiny "point" (singularity), This "point" was smaller than an atom (i.e. smaller than a ten millionth of a millimeter) The Big Bang is the beginning of time and the beginning of space.
Where does the tiny "point" from which the big bang originated come? >>> The scientists say: "We do not know" Because where is no space and no time, you cannot know anything. >>> Some religious scientists say "We don't know - but I believe that a spiritual force (God) caused the Big Bang and thus created the universe. The further development of the universe later also made possible the creation of a life-friendly earth and the emergence of man. |
|
|
|
2. Huge gas clouds are formed
The Big Bang produces a very hot plasma (many billions of °C hot), in which the atoms of the lightest gases are formed: hydrogen and helium. Due to the expansion the gas cools down and there are millions of years only a "dark universe": without glowing gas clouds and without stars. |
|
|
|
3. Stars and Galaxies (= Spiral clouds of stars) are formed
The giant gas clouds condense by attraction (gravitation) in some places and form large gas spheres, which become at least 15 million degrees hot inside due to the weight pressure. At this temperature the atomic fire ignites (hydrogen is transformed into helium) - and the gas ball starts to shine as a star (some billions of years long - like our sun)
|
|
|
|
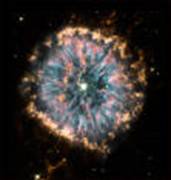
4. Star explosions: Dust clouds are formed
Very large stars (giant stars) have the ability to transform the light gases into heavier elements by atomic-nuclear fusion due to the great heat inside them (several 100 million degrees). When a giant star is burned out, it collapses, becomes much hotter and explodes in a "Super-Nova". This extreme heat also produces all the heavier elements (stones and metals of all kinds), which are now thrown out into space as huge clouds of dust. Such dust clouds can later become solid planets like our earth. Our solar system with solid planets is thus partly formed from the cooled explosion clouds of giant stars. Giant stars must "live" and "die" in order to "give" the material for an earth to the universe. |
|
|
|
5. New stars with solid planets are formed In the outer regions of the Milky Way there are still many gas clouds from the Big Bang (hydrogen and helium) that have not yet clumped together in stars. There new stars are formed in some places. Where the old gas clouds are mixed with the ash (dust and stones) of exploded giant stars, the formation of new stars can also lead to the formation of solid planets, which rotate around the star, like our earth around the sun. Planets are only tiny remnants of the dust cloud, which were not "swallowed" by the forming star due to their special speed and direction of flight. (Cf.: Mass of the sun = about 300,000 times the mass of the earth) |
|
|
|
6. The earth is emerging The dust particles from the ashes of burnt-out, exploded giant stars stick together and become stones and rocks (some up to the size of giant meteorites, comets and asteroids - several meters to hundreds of kilometers in size). Where the largest chunks have clumped together, other parts close to the same orbit also collect by attraction. Thus the planet grows and is heated up by the impact of the meteorite rain to a glowing ball. Later, the surface slowly cools down and forms a solid crust. The comets bring - like huge "dirty snowballs" - the water to the earth. |
|
|
||
|
>>HOME |
||
|
>> Wo kommt die Erde her? Link to share: https://hanglberger-manfred.de/en-erde-entstehung.htm
|
||